The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) Countries
An Overview
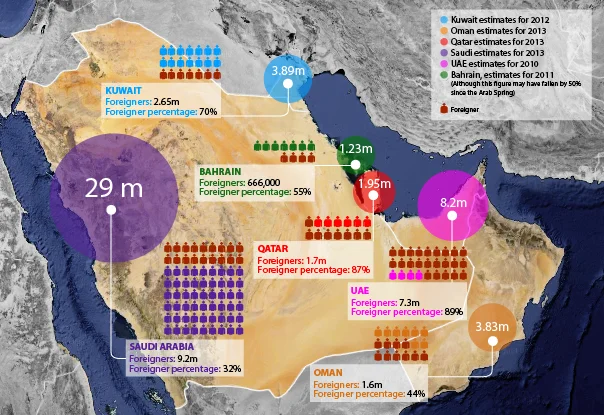
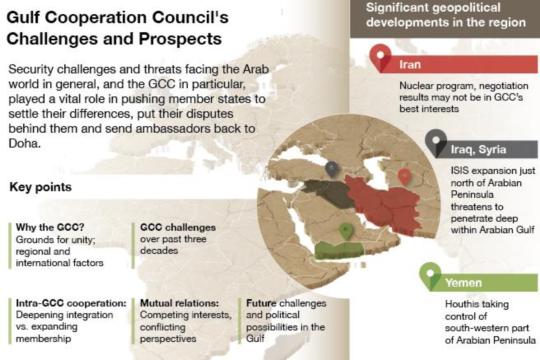
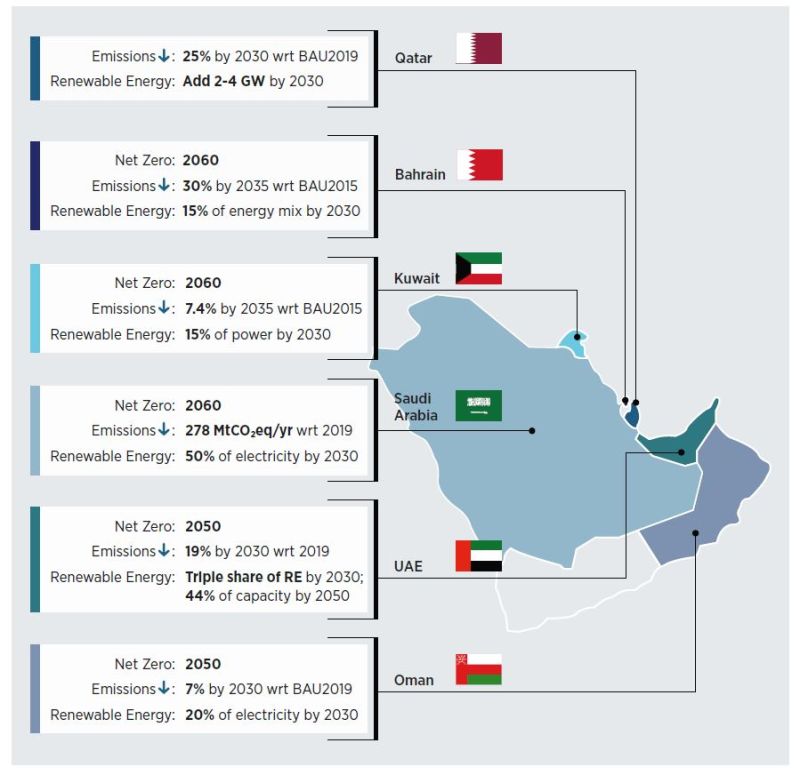
The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) is a regional political and economic alliance consisting of six Middle Eastern countries: Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Established in 1981, the GCC aims to foster economic, political, and security cooperation among its member states. These countries share historical, cultural, and economic ties, as well as strategic importance due to their vast oil and gas reserves.